Homozygous and Heterozygous Genes and Disease
Genetic traits have a significant impact on our predisposition to disease. Genetic testing can offer an array of preventive measures as well as insight into inherited disease. This insight can also provide clinicians with the most appropriate and effective treatment methods to manage disease and improve patient outcomes.

Genetics have a huge role to play in how we look and function. This being said, they also determine the likelihood of developing disease. They are the warehouse of information used to build and maintain cells, as well as dictate what traits get passed along.
The question is, why not use this information and study it in order to direct our patients in a manner that will determine a better future for them?
As our knowledge of the inner workings of the human body expands, so do the capabilities of modern medicine.
The difference between an allele and an SNP
An allele is basically, a variant form of a given gene or SNP (Single nucleotide polymorphism). Meaning it is one of two or more (but mostly two) versions of a known alteration at the same place of a chromosome. Simply put, SNP describes the location, while an allele describes the different version of that alteration.
If you go through the SNP database, you’ll generally see two different alleles. Some SNPs do have three alleles but that would be in the minority.
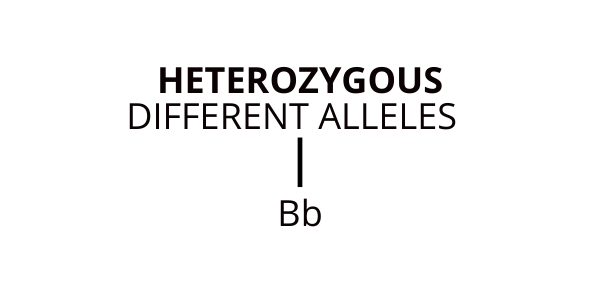
Homozygous and Heterozygous Alleles
Homozygous means that you have two copies of the same allele for that gene.
Heterozygous means that you have two different alleles for a given gene (one from the mother and one from the father).
To put it into layman’s terms, Homozygous essentially refers to two things being the same and Heterozygous refers to two things being different or distinct. The same is applied when speaking about alleles, in which letters are used to represent the dominant and recessive genes.
In alphabetic terms, dominant genes are expressed in capital letters and recessive genes are expressed in lowercase letters. Refer to the images below for a visual representation of heterozygous and homozygous.
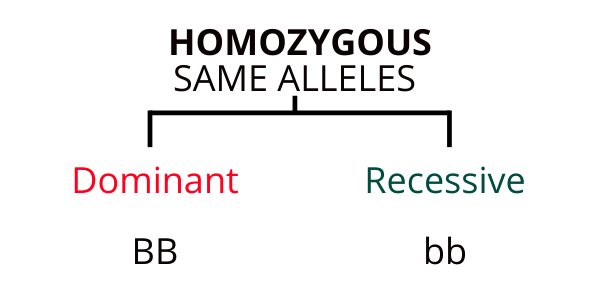
Homozygous is split between dominant and recessive genes. If you’re homozygous for a dominant or recessive gene, because the alleles are identical, the same allele will be expressed either way.
Heterozygous involves two different alleles for a specific gene, one being dominant and the other being recessive. The dominant allele will be expressed and the recessive gene will be masked.
Homozygous genes and disease
There are some diseases that are caused by mutations of the alleles. The risk of disease is usually related to the interaction between dominant and recessive genes. If the allele is recessive, it will not cause disease in people who are heterozygous for that specific gene mutation. The dominant allele will be expressed and you will be a carrier of the recessive gene. If a person is homozygous for a recessive mutated gene, the risk of developing disease is much higher.
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis is an inherited gene disorder that causes complications in the lungs, digestive tract and other vital organs. This usually results in symptoms like frequent lung infections and cysts, pancreatic damage and issues related to digestion.
The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) is a transmembrane protein responsible for the movement of fluids in and out of cells. Those living with cystic fibrosis have inherited two copies of a mutated CFTR gene and are homozygous for this mutation.
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is a disease that causes the build up of the amino acid phenylalanine in both the blood and tissues. This leads to a variety of issues like skin irritability and rashes, neurological degeneration and psychiatric disorders, as well as hyperactivity. People living with the disease need to monitor their diets for phenylalanine, in order to restrict the overconsumption of protein rich in this amino acid.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is caused when an individual is homozygous for a phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) mutation. The PAH gene codes for cells to generate phenylalanine hydroxylase that breaks down the amino acid, phenylalanine. Those living with PKU suffer because their cells cannot generate phenylalanine hydroxylase, and this causes phenylalanine to build up in tissues and blood.
Summary
Genetic traits have a significant impact on our predisposition to disease. Recessive and dominant genes have an influence on our susceptibility to developing a disease and determine whether we are a carrier for a genetic disorder.
Genetic testing can offer an array of preventive measures as well as insight into inherited disease. This insight can also provide clinicians with the most appropriate and effective treatment methods to manage disease and improve patient outcomes.
How do I Become a Functional Medicine Practitioner to learn more about homozygous and heterozygous genes?
The Institute of Integrative Medicine is a global leader in the field of Preventive and Integrative Medicine Education. We offer certified online courses helping you to take charge of your practice and improve the quality of life for your patients. Integrative medicine has the potential to transform healthcare. Find out more about the courses we offer today!
More posts in this category:
Lyme Disease: “The Great Imitator”
Lyme disease, a bacterial infection transmitted by ticks, is often called “the great imitator” due to its wide range of symptoms that mimic other common illnesses. This makes diagnosis challenging, especially in the early stages where symptoms like fatigue, fever, and muscle aches can be mistaken for the flu or other minor conditions. Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing long-term health issues.

An Integrative Approach to Amino Acids
Amino acids are integral in several bodily functions. They are the building blocks of proteins that aid in multiple functions on a cellular level. We cannot forget about crucial amino acids, as they aid in immune function, muscle growth and recovery, and can be utilised in treating deficient hospitalised patients. Amino acid testing and supplementation can improve lifestyle and wellbeing.

How Amino Acids can improve your Exercise Regime
Branched-chain amino acids are extremely valuable for exercise, muscle preservation and growth. Not only can they reduce muscle loss and damage, they can also help grow and repair muscle. Consuming BCAAs can improve strength, endurance and reduce fatigue during exercise.