What is Functional Medicine? Basic principles and definitions
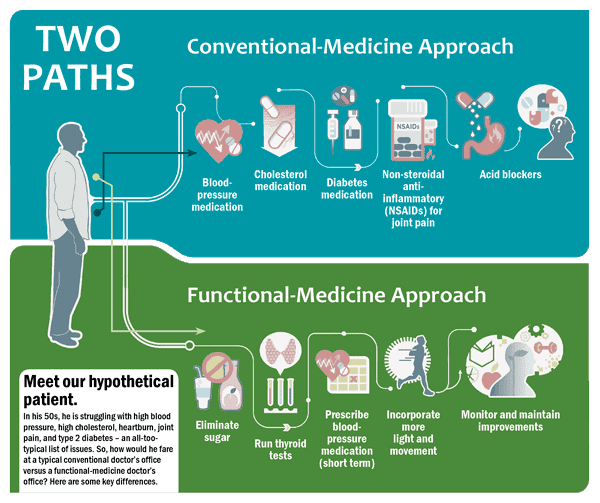
Functional Medicine’s aim is to find out what disturbs the equilibrium within the body, in other words: what is preventing optimal functioning. The symptoms are not treated in isolation, as is often the case with conventional medicine.
Functional medicine brings together conventional medicine with safe and effective complementary medicine. It emphasises the importance of the doctor-patient relationship and the use of all appropriate therapeutic approaches, healthcare professionals and disciplines to achieve healing and optimal health.
What is Functional Medicine? Every patient’s needs are looked at individually. The symptoms are not treated in isolation, as is often the case with conventional medicine.
Often, the cause of the disease is an underlying imbalance or dysfunction of bodily systems. Functional Medicine aims to dig deeper to reveal the true cause of the patient’s health problems. Long term relief cannot be achieved by merely treating the symptoms of an ailment, the underlying root cause has to be identified.
Functional Medicine’s aim is to find out what disturbs the equilibrium within the body. In other words: what is preventing optimal functioning. The functional approach wishes to identify what causes a malfunction within the body and what the body needs to help it function at its best.
5 basic principles that define Functional Medicine:
1. Functional Medicine principles rely on evidence-based medicine
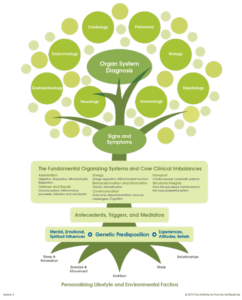
The latest research shows that what happens within us is connected in a complicated network or web of relationships. Understanding those relationships allows us to see deep into the functioning of the body.
Using scientific principles, advanced diagnostic testing, and treatments other than drugs or surgery, Functional Medicine restores balance in the body’s primary physiological processes. This will be your first step to under stand what is functional medicine.
2. Functional Medicine views us all as being different
Genetically and biochemically unique, treating the individual, not the disease. It supports the normal healing mechanisms of the body, naturally, rather than attacking disease directly.
3. Your body is intelligent
Your body has the capacity for self-regulation, which expresses itself through a dynamic balance of all your body systems.
4. Health is not just the absence of disease
To be healthy does not just mean that you do not have any active diseases, but your body is in a state of immense vitality. It is therefore important to see what the body is lacking to enhance it’s functioning.
5. Your body has the ability to heal.
After reading the above steps you should have a good understanding of what is functional medicine. The human body is equipped with all the necessary tools to prevent the onset of the diseases of ageing, with the correct support.
Functional Medicine follows a different route:
The practitioner will conduct physical examinations, such as nail inspection, ankle-brachial reflex and Chapman reflex points relevant to the imbalances identified in the patient history.
Laboratory tests
Advanced laboratory tests are conducted to look into a patient’s physiology and identify imbalances where necessary. These imbalances are addressed, resulting in less severe symptoms, renewed health and well-being.
Some of these tests may be covered by medical aids and used in conventional medicine, others use specialised laboratories including DNA, mitochondrial, stool and saliva analysis.
Treatment plan
Finally, the practitioner will apply a treatment plan that utilises various modalities, including supplementation, coaching and/or therapy, multi-disciplinary referrals, co-ordination of care and regular follow-up visits using outcome-based tools.
These modalities are used alongside conventional medical consultations, and may lead to adjusted or reduced prescribed medications.

“The good physician treats the disease; the great physician treats the patient who has the disease.”
— Sir William Osler
Individualised treatments to answer the question: What is functional medicine?
An important point to remember is the individualised nature of Functional Medicine treatments. Patients with similar symptoms may have different treatment plans in accordance with their medical history and laboratory tests.
Relevant factors to consider are a patient’s unique results influenced by:
- Negative emotions such as fear, greed, anger and envy
- Toxic chemicals in the body
- Pathogenic bacteria
- Parasites and
- Viral pathogens
Summary
Functional Medicine is a holistic approach to health care that addresses the underlying causes of disease. It is an individualised healthcare approach that empowers doctors and patients to work together to identify and treat the root causes of disease.
The practice of functional medicine is based on the integration of the best of science-based and alternative health care. It is a patient-centered approach that aims to restore health and vitality by addressing the root causes of disease based on the patient’s medical history and laboratory tests.
How do I Become a Functional Medicine Practitioner?
The Institute of Integrative Medicine is a global leader in the field of Preventive Medicine Education. We offer certified online courses helping you to take charge of your practice and improve the quality of life for your patients. Find out more about the courses we offer today!